Introduction:
India's agricultural sector stands as a pivotal pillar of its economy, providing livelihoods to millions and supplying essential food resources to its burgeoning population. However, the sector grapples with escalating challenges, notably the diminishing availability of cultivable land due to rapid urbanization and industrialization. As land scarcity intensifies and traditional farming methods struggle to meet increasing demand, the imperative for innovative solutions becomes evident. In this context, vertical farming emerges as a transformative approach poised to revolutionize India's agricultural landscape.
Advantages of Vertical Farming:
Vertical farming, characterized by its utilization of vertically stacked layers for crop cultivation, presents a paradigm shift in agricultural practices. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies and sustainable techniques, vertical farms offer a plethora of advantages over conventional farming methods. According to the World Economic Forum, innovations in production technology have made vertical farms a viable alternative, surpassing 2,000 in the United States alone. These farms boast superior efficiency, significantly reducing water usage by 70% to 95% compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, their versatility allows them to be situated within various structures such as buildings or shipping containers, maximizing land utilization.
Market Growth and Trends:
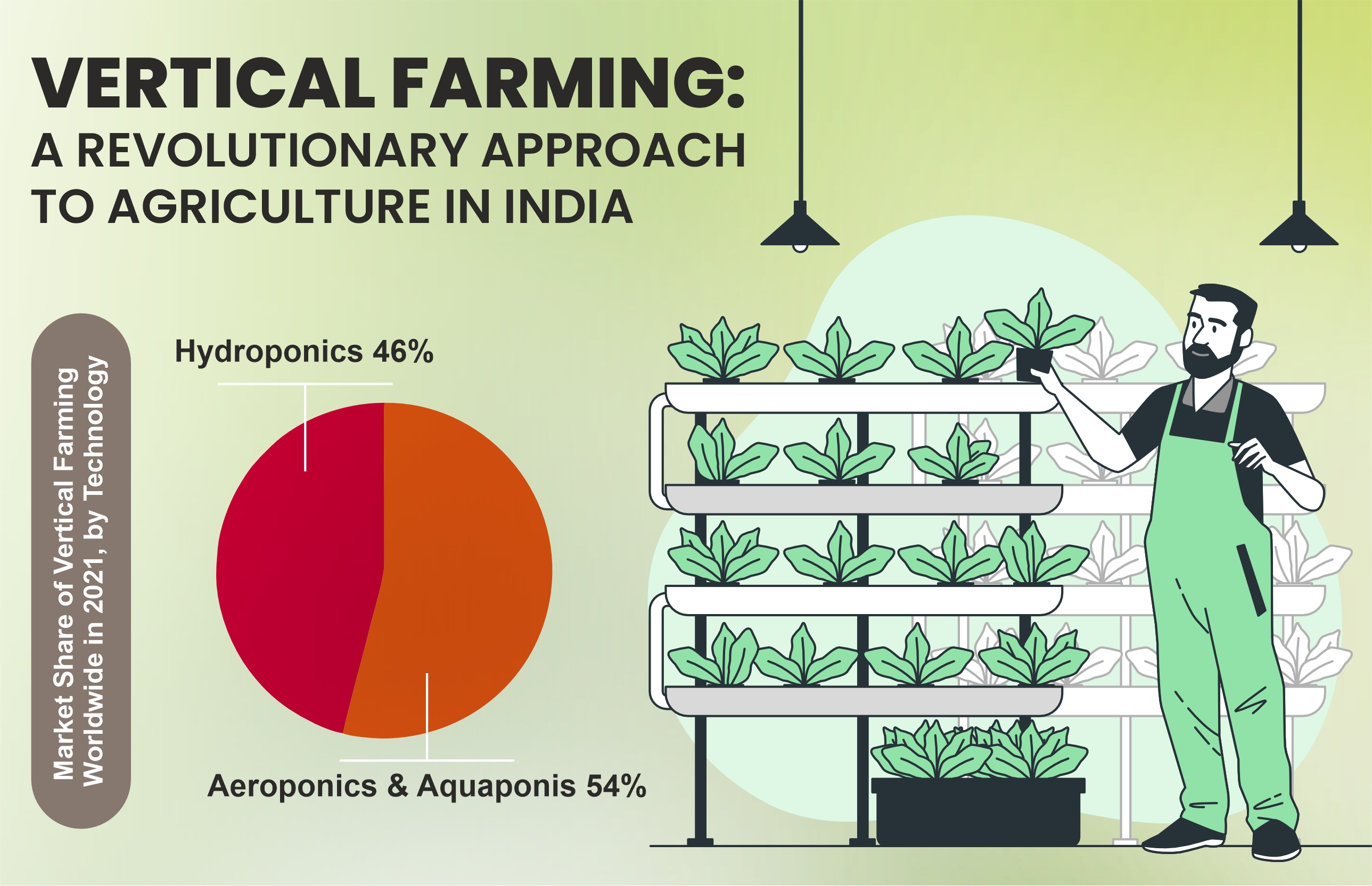
In recent years, the vertical farming industry in India has witnessed remarkable growth, with research indicating a projected expansion at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) exceeding 20% between 2021 and 2026. Among the various vertical farming systems, hydroponics has emerged as a dominant player, commanding the majority of market share due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This exponential growth underscores the sector's potential to address pressing agricultural challenges while fostering economic development.
Types of Vertical Farming Solutions:
Vertical farming encompasses a diverse array of setups and techniques tailored to meet specific agricultural requirements. From conventional building-based farms to innovative methods like hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics, each approach offers unique advantages in terms of resource utilization, crop quality, and scalability. Integration of advanced technologies, including automated irrigation systems and sensor-based crop monitoring, further enhances operational efficiency, enabling precise data-driven decision-making.
Types of Vertical Farming Solutions:
- Hydroponics: Hydroponics represents a soil-less method of plant cultivation that relies on nutrient-rich water solutions to nourish crops. In this system, plants are suspended in a nutrient solution, allowing their roots to absorb essential minerals directly. Various aggregate substrates and growing media, including vermiculite, coconut coir, or perlite, support plant growth and root development. Hydroponic systems come in diverse configurations, including nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics, each offering unique advantages in terms of water efficiency, nutrient delivery, and crop yield. Commercial enterprises, small-scale farmers, and even hobbyists utilize hydroponic production systems to cultivate a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, and strawberries.
- Aquaponics: Aquaponics integrates hydroponics with aquaculture, creating a symbiotic ecosystem where plants and fish mutually benefit from each other's presence. In this closed-loop system, fish waste serves as a natural fertilizer for plants, providing essential nutrients for growth, while plants purify the water, creating a conducive environment for fish. The nutrient-rich water circulates between the fish tanks and the hydroponic beds, promoting sustainable and efficient cultivation of both crops and aquatic species. Aquaponic systems offer numerous advantages, including enhanced nutrient cycling, reduced water consumption, and the production of both vegetables and fish in a single integrated system. This holistic approach to farming holds particular relevance in urban environments, where space constraints and environmental concerns drive the need for innovative agricultural solutions.
- Aeroponics: Aeroponics represents an advanced method of plant cultivation that utilizes a mist or aerosol of nutrient-rich water solution to nourish plant roots suspended in air. Unlike hydroponics, which submerges plant roots in a nutrient solution, aeroponics delivers nutrients directly to the roots through periodic misting or spraying. This precise delivery method ensures optimal nutrient uptake and oxygenation, promoting rapid and vigorous plant growth. Aeroponic systems are highly efficient, requiring minimal water and nutrient inputs compared to traditional soil-based cultivation methods. By suspending plants in the air and exposing their roots to oxygen-rich mist, aeroponics maximizes growing space and minimizes resource wastage, making it an ideal solution for vertical farming applications.
Cost and Budget Considerations:
Establishing a vertical farm in India entails a significant initial investment, influenced by factors such as technology adoption, scale of operations, and infrastructure development. Estimates suggest that the cost of setting up a vertical farm can range from 50 lakhs to 1 crore rupees per acre, encompassing expenses for infrastructure, lighting, irrigation systems, and other essential components. Additionally, an annual operating budget ranging from 5 to 10 lakhs rupees per acre covers ongoing expenses like power consumption, water supply, labor wages, and maintenance costs.
Competitive Landscape:
The Indian vertical farming sector is characterized by intense competition among both established players and emerging startups. Major competitors such as Fresher Underwater Farms Private Limited, Future Farms LLP, Triton Foodworks Private Limited, and Altius Farms Private Limited vie for market share through strategic alliances, technological innovation, and differentiation strategies. This competitive environment fosters continuous advancements in vertical farming practices, driving industry growth and fostering consumer choice.
Profitable Crops in Vertical Farming:
Vertical farming offers lucrative opportunities for cultivating high-value crops that command strong market demand and premium prices. Crops such as tomatoes, strawberries, mushrooms, and peppers are particularly well-suited for vertical cultivation, owing to their profitability and adaptability to soil-less growing techniques. However, the versatility of vertical farming enables farmers to explore a wide range of crops, tailoring their selections based on factors such as regional demand, climate conditions, and resource availability.
Government Support and Initiatives:
Recognizing the transformative potential of vertical farming, both the central and state governments have introduced various initiatives to support and incentivize its adoption. Programs such as Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) and National Horticulture Mission (NHM) aim to promote water-saving technologies and infrastructure development, aligning with the water-efficient practices inherent to vertical farming. Additionally, initiatives like StartUp India seek to nurture entrepreneurial growth and innovation, providing financial assistance, mentorship, and regulatory support to aspiring vertical farming entrepreneurs.
Conclusion:
Vertical farming stands at the forefront of agricultural innovation, offering a sustainable and scalable solution to India's pressing agricultural challenges. With its potential to maximize land utilization, conserve water resources, and enhance crop productivity, vertical farming holds immense promise for transforming the Indian agricultural landscape. Through continued technological advancements, strategic government support, and collaborative efforts across the public and private sectors, vertical farming is poised to usher in a new era of agricultural prosperity and food security for India.